4. Data Analysis
Evaluating data using analytical and statistical tools to discover useful information and aid in business decision making.
 Analysis Preparation
Analysis Preparation
CLEANING. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to skewed results. Analysts clean data sets by removing invalid entries or duplicate information, for example.
AGGREGATION. Raw data may be collected and stored in several different formats. Data aggregation is the compiling of information from different data sets so that data analysis tools can import it and work with it.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS. The most common type of analysis, it involves closely examining mostly quantitative data to identify trends.
Standard analyses include the arithmetic mean, standard deviation, regression and hypothesis testing.
TEXT ANALYSIS. Semi structured or unstructured data in the form of narrative texts can be analysed by “parsing” the texts to extract machine-readable data pieces.
DATA MINING. If you’re working with very large data sets, data mining uses machine learning, artificial intelligence and statistics to find patterns and correlations to predict outcomes.
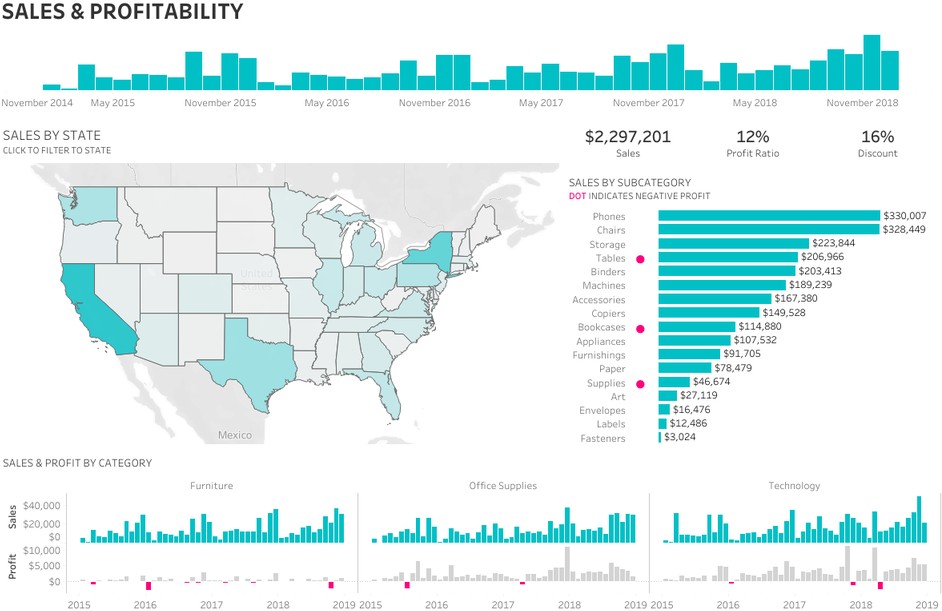
VISUAL ANALYTICS. To identify outliers, gaps, trends and interesting data points, many analysts build charts and visual representations that provide various perspectives and point to areas that warrant further investigation.
Evaluating data using analytical and statistical tools to discover useful information and aid in business decision making.
WHAT TO LOOK FOR
FACTS
- Numbers which offer a high level summary of your
- Provide “nice to know” information and help you familiarize yourself with your data set.
EG.
- 100 recipients
- 50 email clicks
- 50% click through rate
STATS
- Basic descriptive statistics such as mean, median, mode, distribution etc.
- Help you better visualize any patterns that may be present in your data ad provide high- level summaries of your variables.
TRENDS
- Comparisons and change over time, within the same group at different points in time or between groups at the same time or at different points in time.
- Combines with facts and stats to reveal more sophisticated patterns. EG. level of satisfaction between two different programs